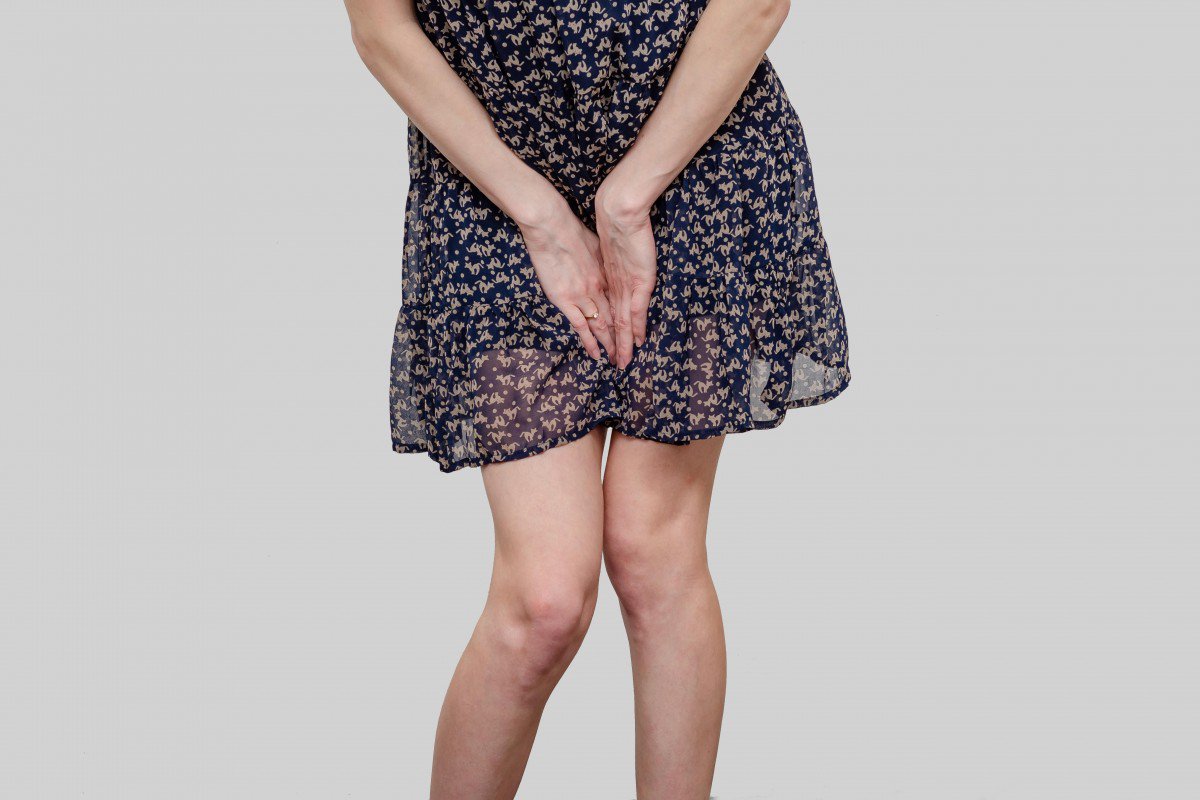
Urinary Incontinence can be termed as an unintentional loss of bladder control and general bladder weakness.
Types of Urinary Incontinence
Functional Incontinence — those immobile who are not originally incontinent fail to get to the toilet in time and are placed in absorbent products and therefore are considered incontinent.
Stress Incontinence — happens when the urethra cannot handle the increased bladder pressure while exercise, coughing or sneezing.
Urge Incontinence — can be caused by an unexpected, reflex bladder contraction. It is the incompetence to delay urinating long enough to get to a toilet when you get the feeling.
OAB Incontinence — is the medical term signifying a group of symptoms resulting from involuntary bladder spasm that includes frequency of urination particularly at night and urgency with or without unintentional leakage.
Overflow Incontinence — occurs when the bladder becomes overly full and overpowers urethral resistance because it can’t be wholly emptied. And also, when there is a frequent leakage of urine without the urge to urinate.
Total Incontinence — results from the total absence of urinary control which may lead to continuous leakage or periodic uncontrolled emptying of the bladder.
What is Stress Incontinence (SI)?
Stress Incontinence is the most common kind of urinary incontinence that occurs during an activity, such as coughing or sneezing. Such an activity causes a small amount of urine to leak from the urethra, which is the tube urine passes through.
It happens to largely affect women, especially, older ones. Additionally, women who have given birth are more likely to have stress incontinence. This particular condition can have a dramatic impact on one’s life! Did you know there are over
3.3 million Canadians experiencing at least one of the different types of urinary incontinence?
What Causes Stress Incontinence?
Stress incontinence marks movements and activities such as coughing, sneezing, and lifting, or others that put greater abdominal pressure on the bladder. Hence, the leakage of urine.
Numerous things can account to stress incontinence. For instance, it can result from weak muscles in the pelvic floor or a weak sphincter muscle at the neck of the bladder. A problem with the way the sphincter muscle opens and closes can also result in stress incontinence.
Chronic coughing, smoking, and obesity may also lead to SI. In fact, any physical changes to the body of a woman can lead to the ailment. Factors that can cause these changes include:
- Pregnancy and childbirth,
- Menstruation,
- Menopause,
- Pelvic surgery,
- Problems with muscles in the bladder, and the urethra, and
- Weakened muscles around the bladder.
When suffering from this ailment, the muscles in the pelvis can weaken. This can cause the bladder to drop down into a position that prevents the urethra from closing completely. And, this results in a leakage of urine.
What Are the Symptoms of Stress Incontinence?
The main symptom of stress incontinence is a leakage of urine at times of physical movement or activity. For example,
- Coughing,
- Sneezing,
- Laughing,
- Standing up,
- Exiting a car,
- Lifting something heavy,
- Exercising, and
- Sexual intercourse.
The leakage may be as little as a drop or two, or probably “squirt,” or even a stream of urine.
How Is Stress Incontinence Treated?
Self-help techniques and aids can be used to treat mild stress incontinence. In addition, there are a number of treatments available for stress incontinence:
Pelvic Floor or Kegel Exercises: Kegel exercises or pelvic floor exercises, are a part of your physiotherapy. These assist to strengthen the muscles that support the bladder, uterus, and bowels. A physical therapist can help you learn how to do them correctly. Just like any other exercise routine, how well Kegel exercises work for you depends on whether you perform them regularly. By doing so, you can reduce or even prevent leakage problems.
While doing these exercises, avoid moving your leg, buttock, or abdominal muscles. These exercises should be done every day, five sets a day. Each time you contract the muscles of the pelvic floor, hold for a slow count of five and then relax. Repeat this 10 times for one set of Kegels.
Manual Techniques: Your physical therapist will perform pressure, massage and stretch techniques on the surface of the muscles in the pelvis, in order to help you contract your muscles more efficiently.
Biofeedback: A probe is placed in the vagina (for women). This probe is able to read the activity of your pelvic floor muscles for display on a screen. It will help you with your training for it allows you to see how well you are performing your exercises.
Electrical Stimulation: As mentioned above, a probe is placed in the vagina or in the anus. Thereafter, an electric current is applied to the muscles to help you feel them and to give you the sensation of a pelvic floor contraction. This will help you to perform the exercises more easily.
Bladder training: It involves teaching people to resist the urge to urinate and to gradually expand the interval between urinating.
Weight loss: Stress incontinence has been linked to obesity. So, regulating what you consume is a must.
Timed Voiding: Record the times that you urinate and when you leak urine. This will give you an idea of your leakage ‘patterns.’ Moreover, now, you can avoid leaking in the future by going to the bathroom at those times.
Medical Devices: Your doctor can insert a device called a pessary into your vagina to stop stress incontinence. A pessary is a ring that, when inserted, applies pressure on the urethra so as to keep it in its normal location. Doing so can decrease urine leakage. Possible side effects from using a pessary include vaginal discharge and infections.
Injections: Bulking agents are substances that are injected into the lining of the urethra. They increase the size of the urethra lining. Increasing the size creates resistance against the flow of urine. Collagen is one bulking agent that is commonly used. If successful, periodic injections may be needed.
Surgery: A surgery is performed when other methods for treating stress incontinence fail to deliver. Now, surgeries are minimally invasive and are performed on an outpatient basis in most cases.
Conclusion
If you suffer from this condition, you may want to see the physiotherapist once or twice for advice followed by a comprehensive treatment plan customized for you.
To do so, reach out to us at RBH Health Physiotherapy and Rehab Centre.